分享:
什麽是 NMN
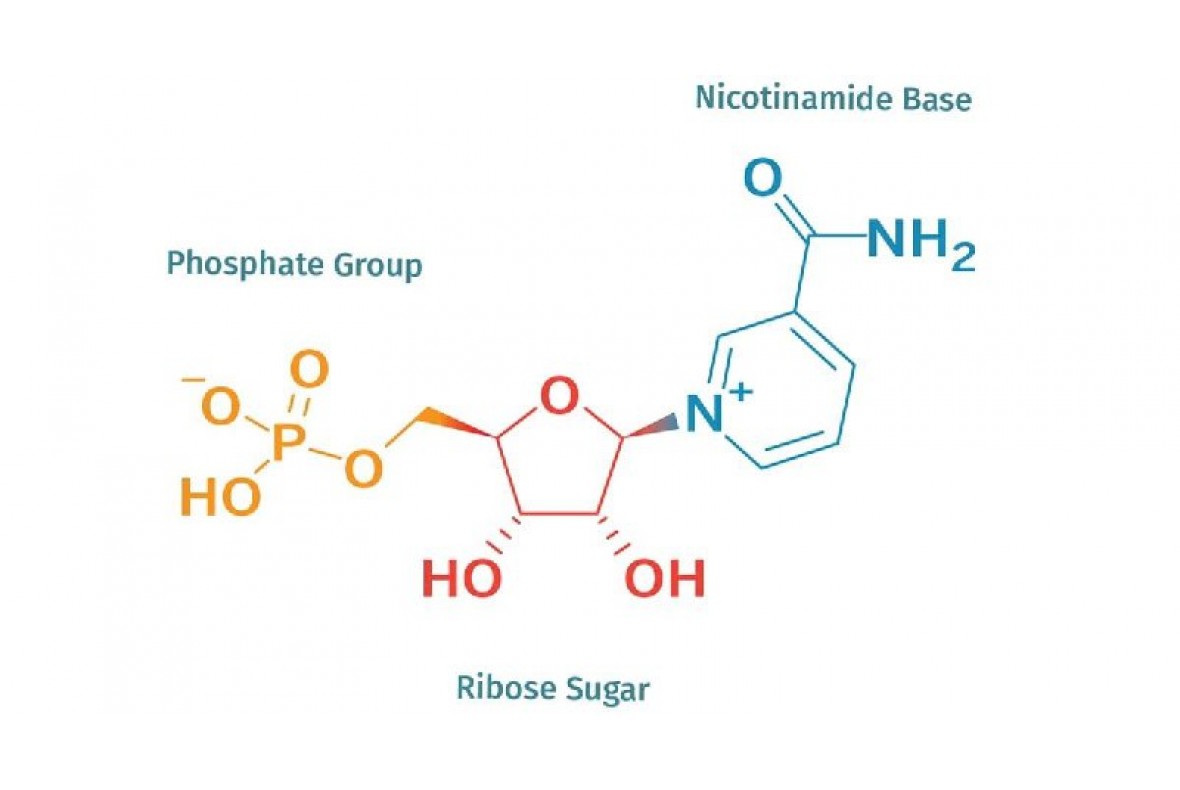
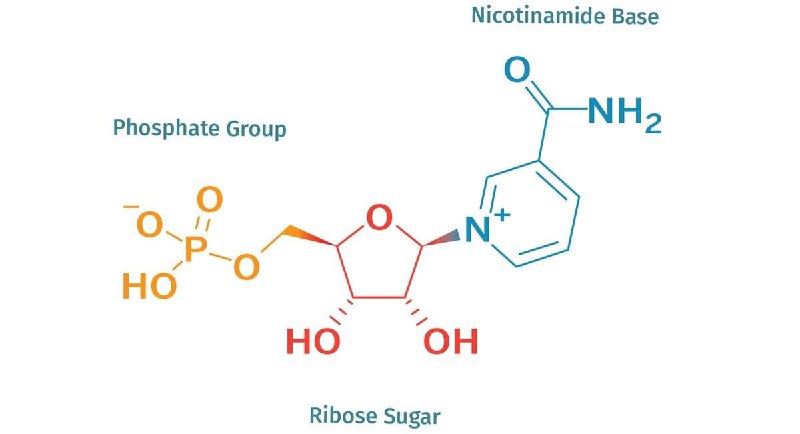
什麼是 NMN ?
NMN 代表煙酰胺單核苷酸,一種天然存在於所有生命形式中的分子。 在分子水平上,它是一種核糖核苷酸,是核酸RNA的基本結構單元。NMN 是生物必需分子NAD+(煙酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸)的直接前體,被認為是增加生物細胞中 NAD+ 水平的關鍵成分。
NMN 抗衰老的功能
哈佛大學生物學和遺傳學教授
Prof. David Sinclair 提出,隨著年齡的增長,人體會失去
NAD+,“以及由此導致的去乙酰化酶活性下降,被認為是我們的身體在年老時會出現疾病的主要原因,而這種情況在我們年輕時是不會發生的。”
Prof. David Sinclair 認為,在衰老過程中增加 NAD+ 水平可能會減緩或逆轉人體某些衰老的過程。而提升人體内 NAD+
可以通過飲食吸收NMN來實現。
NMN 和 提升運動耐力
研究發現,口服
NMN 粉末可以增加成年跑步者的肌肉對氧氣的消耗能力。 更重要的是,服用NMN
還提高了人體骨骼肌利用氧氣在耐力運動中更有效地產生能量的能力。此外,研究也發現,NAD+
是維持人體健康的線粒體功能和穩定能量輸出的關鍵之一。而提升人體内 NAD+ 可以通過飲食吸收NMN來實現。
直接服用NAD+ 來提升體内 NAD+ 的數量可以嗎?
哈佛大學生物學和遺傳學教授
Prof. David Sinclair 提出,“直接向生物體餵食或施用 NAD+ 並不是一個可行的選擇。
NAD+分子不能輕易地穿過細胞膜進入細胞,因此不能對新陳代謝產生積極影響。 相反,必須使用製造 NAD+ 的前體分子來提高 NAD+ 的水平。”
這意味著 NAD+ 不能用作直接補充劑,因為它不易被吸收。 NAD+ 前體NMN更容易吸收,是更有效的補充劑。
人體利用NMN來製造NAD+(煙酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸 )
我們的身體自然地會從較小的成分或前體中產生
NAD+。 人體內有五種主要的前體:色氨酸、煙酰胺 (Nam)、菸酸 (NA 或菸酸)、煙酰胺核苷 (NR) 和煙酰胺單核苷酸 (NMN)。
其中,NMN 代表 NAD+ 合成的最後步驟之一,它和其它前體都可以來自飲食。 一旦進入體內,我們的細胞就可以通過幾種不同的途徑合成
NAD+。此外,向體内直接注入NMN也可導致身體許多部位的 NAD+ 增加,包括胰腺、脂肪組織、心臟、骨骼肌、腎臟、睾丸、眼睛和血管。
在實驗中,小鼠口服 NMN 可在 15 分鐘內增加肝臟中的 NAD+。
NAD+ 有什麼作用?
NAD+是人體內除水以外含量最多的分子,沒有它,有機體就會死亡。NAD+
在生物體代謝過程中發揮著特別積極的作用,例如糖酵解、TCA 循環(AKA
克雷布斯循環或檸檬酸循環)和電子傳遞鏈,這些功能發生在生物的線粒體中(線粒體是細胞的動力源,負責產生我們身體使用的化學能),是生物(包括人類)獲得細胞能量的方式。
什麽是 DNA
DNA,脫氧核醣核酸(英語:deoxyribonucleic
acid,縮寫:DNA),又稱去氧核醣核酸,是一種生物大分子,它引導生物發育與生命機能運作,也可組成遺傳指令。隨著生物體年齡的增長,它們會因輻射、污染和不精確的
DNA 複製等環境因素而產生 DNA 損傷。 根據目前的衰老理論,DNA損傷的積累是衰老的主要原因。
我們為什麼要關心 NAD+
自
1906 年發現 NAD+ 以來,該分子因其在體內的豐富性及其在保持我們身體運轉的分子途徑中的關鍵作用而受到科學家的關注。
在動物研究中,提高體內 NAD+
水平已在代謝和年齡相關疾病等研究領域顯示出可喜的成果,例如糖尿病、心血管疾病、神經退化性疾病和免疫系統普遍下降疾病等等。
NAD+
在生物體内另一個重點是, 它是生物體内負責修復受損 DNA的Sirtuins(一個酶,enzyme,家族)的能量來源。
Sirtuins也被稱為
“基因的守護者”,在維持生物體内細胞健康方面發揮著至關重要的作用,它參與生物體内細胞應激反應和損傷修復,胰島素分泌、衰老過程和
神經退化性疾病和糖尿病等人體内部活動。 當人體失去足夠的NAD+
,Sirtuins會停止修復受損DNA,或修復變得非常緩慢,這就像汽車沒有燃料就無法行駛一樣。保持Sirtuins 的活動需要 NAD+。
NAD+ 有助於控制和修復 DNA 損傷
老年人的 NAD+ 水平降低是因爲正常老化過程導致的 DNA 損傷累積導致NAD+ 濃度降低。人體中任何進一步的 DNA 損傷都會加劇這種消耗。幾乎所有細胞都含有修復這種損傷的“分子機制”。 這種機制的運用消耗大量的 NAD+ 和能量分子。
NMN 和 增强免疫系統
隨著成年人年齡的增長,免疫系統下降,人們更容易生病,人們更難從季節性流感甚至
COVID-19 等疾病中恢復過來。 最近的研究表明,NAD+ 水平在免疫反應和衰老過程中調節炎症和細胞存活方面發揮著重要作用。 該研究強調了
NAD+ 對免疫功能障礙的治療潛力。
NMN 和 心臟功能
提高
人體内 NAD+ 水平可以保護心臟並改善心臟功能。 高血壓會導致心臟擴大和動脈阻塞,從而導致中風。 在利用小鼠的研究中發現,NAD+
增強劑補充了心臟中的 NAD+ 水平,並防止了因血流不足而導致的心臟損傷。 其他研究表明,NAD+ 增強劑可以保護小鼠免受心臟異常增大的影響。
NMN 副作用和安全性
NMN 在動物身上被認為是安全的,其結果很有希望,以至於人體臨床試驗已經開始。 這種分子在很大程度上被認為是安全且無毒的,即使在小鼠和人體研究中使用的濃度很高。
最新帖子
09 January 2023
|
12:01 am
09 May 2019
|
02:05 pm
02 May 2019
|
01:05 am
22 January 2019
|
12:01 pm
22 January 2019
|
12:01 pm
22 January 2019
|
12:01 pm
22 January 2019
|
12:01 pm
01 May 2019
|
06:05 pm